Jan 07, 2024
Shaping the Future of the Digital Product Passport
eBook
Near Field Communication (NFC) can play an essential and valuable role in delivering the regulatory requirements set out to achieve a circular economy. Through ensuring easy access to information on how a product and its components can be recycled, NFC technology can support a global approach to ensuring the sustainable consumption of resources.
Almost every standards body today is specifying NFC technologies as a data carrier to connect products to DPP data. NFC Forum plans to leverage this and data content standardization efforts by ISO and others, to fulfil its role in the circular economy.
The current Digital Product Passport (DPP) initiative is expected to be the future information system of the circular economy, enabling data sharing around re-using, remanufacturing and recycling materials. Using NFC for DPP is optimizing a component already in billions of devices, which is key to achieving sustainability.
Contents

The role of NFC technology in the circular economy
Every day millions and millions of people use NFC technology to connect to the world around them. It’s a proven super-fast and secure way to pay for things, ride the train, unlock a door and start your car.
But NFC can do so much more. It is active in countless markets and regularly makes news headlines with the innovative ways it continues to enhance businesses operations and lives of consumers.
The success of NFC technology is largely due to its slim design, security capabilities, data storage integrity and familiarity to users.
It is thanks to these key attributes that NFC technology can play an essential and valuable role in the delivery of the Digital Product Passport (DPP).
The NFC community is collaborating to define a standard that supports the regulatory requirements of the DPP, which supports sustainability of materials and encourages a global approach to the circular economy.
The DPP is expected to be the future information system of the circular economy.
The Digital Product Passport (DPP) is an initiative that is essential in achieving a circular economy which can effectively operate at scale. Companies globally are incorporating DPP requirements into their core products and, most notably, DPPs form part of Europe’s Green Deal. This program aims to transform the European Union into a modern, resource-efficient and competitive economy that is climate neutral.
The European Commission recognizes that the DPP is key to promote a functioning circular economy, which in turn encourages sustainable consumption to minimize waste and keep resources within an economy for as long as possible.
Standardizing Product Information
By ensuring relevant parties can access information on how a product and its components can be recycled, remanufactured and contribute to the circular economy, the DPP:
- Enables manufacturers and consumers to make sustainable product choices and promote sustainable production methods.
- Optimizes and extends product (and component) usage.
- Provides new opportunities to extract and re-use valuable materials.
- Shares reliable, relevant and verified product material information.
- Supports various stakeholders to verify sustainability compliance.
- More widely, the DPP is a unique opportunity to standardize how a product can be tracked throughout its lifecycle.
What is an NFC Tag?
NFC Tags are small enough to integrate into most products; posters, clothing, business cards, prescription bottles. The tags are passive, which means they don’t have a power source, never need a battery, but operate by harvesting power from the device that reads through magnetic induction.
What value can the Forum bring to the DPP initiative?
Through its community, standards, and certification program, the Forum can bring stability, continuity, and reliability to the DPP initiative.
Leveraging Reader/Writer Mode on consumer handsets.
NFC Forum Standards enable NFC technology to work in many ways to support a variety of operations. Most product designers and users are unaware of these capabilities.
For instance, when you make a payment with your mobile phone, you are using Card Emulation mode where the payment terminal believes your phone is just a static card.
NFC Reader/Writer mode allows your phone to directly read and write information from/to NFC tags. Mobile application developers can design custom applications that can interact with NFC tags and other devices both reading and then writing data over the tap-based connection. This mode also allows devices to read tags that can include URL addresses, contact info, or automations.
And for completeness, the NFC Forum Standard also includes a Wireless Charging mode as well.
We see a future where consumers, regulators, and system providers can use the mobile phone they already own to read DPP data from the cloud or directly from products. No special readers, no aligning cameras, and even without an internet connect, we see a bright future for NFC technologies in the DPP ecosystem.
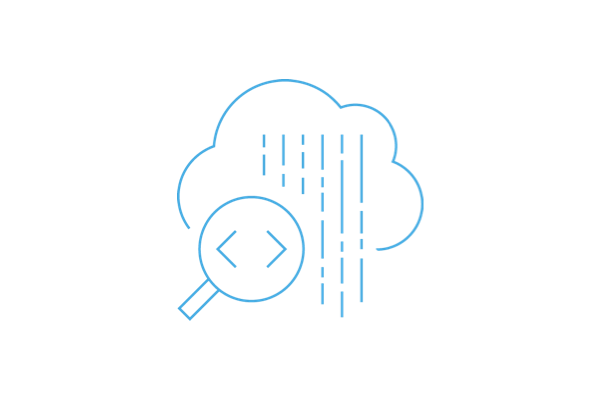

NFC can act as the data carrier to link products with their online DPP data and unlike other RF technologies can be read by billions of consumer mobile phones.
1. Accessing Cloud-based DPP Data
The initial information designs being considered for DPP data are centered around cloud-based systems. Data carriers, as they are known, are unique links from products to a DPP that can be implemented as QR codes or NFC tags.
In the same way you can read a restaurant menu or tap a business card, anyone could access a DPP stored in the cloud through these familiar interfaces.
The system architecture of the DPP is designed to:
- Host DPP data online in the cloud.
- Products use a ‘data carrier’ such as a QR Code or NFC to link to the DPP data.
NFC can act as the data carrier. An NFC tag or a Card Emulator device can be used to link products with their online DPP data.
Embedding the DPP will ensure data is available throughout a product’s entire lifecycle and promotes circulatory goal success.
2. Permanently attach DPP data to a product
While hosting DPP data online in the cloud is suitable for many products and use cases, it presents challenges for longer term validation and integrity of DPP data. For example, if a business manufacturing / selling the product ceases to operate, they may be unable to continue ‘hosting’ and ‘maintaining’ the DPP online portal.
There is also a fixed operational and carbon footprint cost for maintaining DPP data online, and having data exclusively cloud-based means that it may be challenging to validate the integrity of online systems over the life of a product.
The NFC Forum is exploring how NFC technology could resolve such issues.
In addition to supporting the direct access to online/cloud DPP data, NFC tags and NFC chipsets could also store data offline by permanently embedding the DPP data directly into a product.
The result is DPP data could be accessed ‘offline’ without having to connect with the internet.
The benefits of embedding DPP data on a product are significant:
- NFC Card Emulator Devices are designed to function the entire service life of a product, whereas care labels and instruction manuals are discarded with first use, disconnecting a product from the circular economy.
- The data can be used to validate the integrity of an online DPP.
- DPP data can be accessed even if a reader is offline.
- There is a transparent and accessible chain of custody throughout a product’s lifecycle to differentiate between authentic and counterfeit products.
With hundreds of millions of NFC-enabled devices in the marketplace today, NFC technology is proven as one of the most versatile and secure technologies available.
For manufacturers, NFC tags and CE devices are robust, have a strong attachment rate and are hard to deface. This increases the likelihood that DPP information remains available throughout a product’s lifecycle, empowering businesses and consumers to make informed sustainable choices when purchasing goods.
Many businesses and consumers worldwide are familiar with using NFC technology. Any ‘consumer off the shelf’ device, such as a smartphone, would allow businesses and consumers to read and access DPP data. This would use the NFC Reader / Writer Mode; a capability which is already built into hundreds of millions of consumer handsets today – and likely already in your hand.
Cost + Convenience = Sustainability
Using NFC for DPP is optimizing a familiar technology already in millions of devices, which is key to achieving sustainability.
Using consumer devices as ‘readers’ to access DPP information, enables businesses, consumers and regulators, to make sustainable decisions and promote their commitment to sustainable practices.
Hundreds of millions of products each year alreadyship with NFC technology embedded, so adding DPP functionality would be a near-zero cost approach towards achieving global sustainability goals and expected future governmental regulations.
For those new to NFC, the slim chipset of the technology means product designers have aesthetic freedom as the size of an NFC chipset is smaller.

Due to the universal adoption of NFC Forum Standards on smartphones and wearables, the NFC Forum is well positioned to define global standards for RFID in DPP.
Role of the NFC Forum
NFC Forum is an active technical community of more than 500 companies. It works collaborativelyto bring all NFC stakeholderstogether – from silicon vendors and OEMs to application developers and implementers – to create an innovative NFC ecosystem which creates solutions that are more accessible, efficient, and beneficial for everyone.
The body is driven by its board which includes Apple, Google, Huawei, Identiv, Infineon, NXP, Qualcomm, Sony, and STMicroelectronics.
NFC Forum has proven success in designing, evolving and regulating global technical specifications. It uses its vast community to access the required expertise, while working with relevant industry partners to align its technology with other standards and solutions. Its legal framework ensures standards are accessible to all from its website.
NFC Forum also has the skills and operational framework to continually evolve its specifications, to support and identify supplementary data on devices and explore new sustainability use cases.
The NFC DPP Specification builds on this secure, reliable, familiar technology, enabling consumers and regulators to read the DPP data using off-the-shelf handsets.
NFC Forum Scope of Work
- Listens to its members and partners to understand future market requirements.
- Defines standards that enable mass market delivery of NFC technology.
- Tests and verifies that products perform to the functional standards expected by NFC Forum.
- And, promotes the use of NFC technology through the Wayfinding Mark.
NFC Forum Standards
- Ensure the quality of NFC products and services and that they are fit for purpose.
- Confirm NFC products and services perform as expected by business and consumers.
- Promote reliability, interoperability and compatibility across NFC products and services.
- Facilitate NFC trade and innovation by removing barriers.
- Promote common understanding and guidance of NFC products and expectations.
NFC DPP Standard
NFC Digital Product Passport (NDPP) will be a standard where chips and tags can store a link to connect products to an online DPP accessed from a standard consumer mobile phone.
Expected functionality:
- Readable by commercial-off-the-shelf smartphones.
- Safely coexist with current NDEF features, mobile behaviors.
- NDPP can be read without requiring power from the product.
- Simple URL links to online/cloud DPP data.
- Future-proof for evolving DPP Standard requirements.
The NDPP Standard also plans to allow some or all DPP data to be directly stored then embedded into products using the same chip or tag used for an online DPP connection.
Expected functionality:
- Full/partial/public DPP data embedded into the product.
- Extended to include additional serialized data.
- Ensures DPP data survives the full life and disposal of products.
- Supplemental data to be written and retrieved.
- Tap location for reading NDPP data to be easily identifiable on product.
- Clear reference to ISO and CEN standards.
The ongoing NDPP goal is to ensure it meets the requirements of the EU DPP regulation and corresponding standardization.
Interested in being part of this discovery process and defining the future of NFC? Join the NFC Forum.
Get Involved
The value of NFC technology to support the DPP is clear. From enabling citizens and authorities with or without an internet connection, to use a ‘common off the shelf’ NFC-enabled handset to tap on NDPP location and retrieve DPP content from a compliant product, to allowing regulators and authorities to validate cloud-based data, NFC has the potential to significantly increase accessibility and longevity of DPP data.
But the potential goes much further. Data retrieved from an NFC DPP could be available to the device operating system for further processing to translate into human readable format, supplement online information, or even integrate with other handset features like GPS for safe disposal locations.
Industrial waste management operations can, on or offline, start to read product NFC DPP data from products to increase efficiency and accuracy of their operations, and start reusing and recycling even more materials.
NFC Forum is committed to understanding how it can further this work, and use its knowledge, community and framework to improve the sustainability of products and solutions. Its commitment goes beyond the DPP initiative, with work also underway to explore how smartphone capabilities can be optimised so more products can be delivered using a mobile device, such as access control, payment and ticketing, as well as encouraging NFC Wireless Charging for small products, removing the need for cables and single use batteries.
BONUS: Industry Introduction to DPP
The Digital Product Passport (DPP) while pioneered in the EU, stands at the forefront of the global sustainability movement – also known as the circular economy. Read NFC Forum's DPP overview.
The DPP is accessibly designed to deliver comprehensive product information for re-use, remanufacturing, and recycling by businesses and consumers.
Experts from leading companies and organizations will address the why the DPP matters, how they see future implementation, and how NFC can be used to amplify the DPP's reach, ensure data authenticity, and promote a truly global circular economy.

