May 02, 2023
Beyond the Barcode: the Case for NFC in Manufacturing
In spite of the shortages brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic, Lean manufacturing is still highly relevant. The difference is that digital technologies are now essential because they provide data-driven and real-time insights into production lines and entire supply chains.
According to McKinsey’s report on the IoT in manufacturing and the pandemic response, “Overall, 94 percent of respondents told us that Industry 4.0 had helped them to keep their operations running during the crisis, and 56 percent said these technologies had been critical to their crisis responses.”
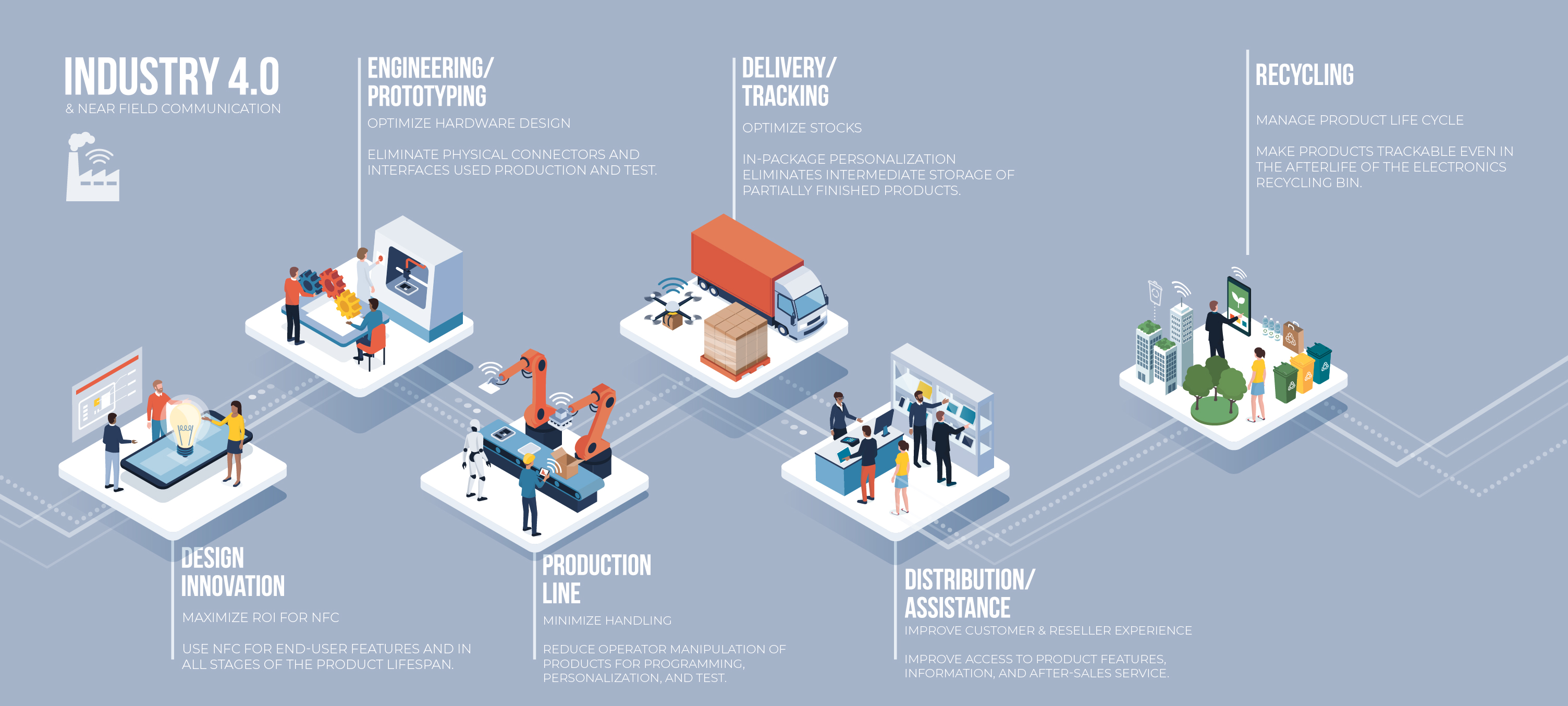
Using NFC in the manufacture of IoT devices isn’t wildly complex, and it can take advantage of simple components. Manufacturers are already accustomed to using barcodes and QR codes on products, for example. But organizations can also take advantage of the expanded capabilities of near-field communication (NFC) tags in their product designs to improve the manufacturing process.
To be clear, we’re not suggesting that manufacturers do away with QR codes or barcodes in all cases, but NFC can make the production line more efficient and cost effective and deliver better value to the organization and customer alike. Use of NFC can even extend the functionality of bar codes in systems without interfering with legacy processes.
Key Advantages of NFC
NFC is really a traceable asset because you are reading actual data that was stored at the time of use, and some tags allow for ongoing communication with users, as you’ll see below.
The overall advantage of NFC in Lean is that it eliminates the need for intermediate storage of unfinished products and materials. This is because it reduces the number of human interventions in the manufacturing process, for example, connecting a cable to set an attribute or parameter. This in turn reduces the amount of space required to store partially assembled goods, and any damage that can occur during storage or human interventions.
Also, it is possible to print out a serialized barcode or QR after packaging. The manufacturers don’t need to keep parts as semi-finished waiting for the final configuration.
For Agile manufacturing, customization of products (for example, setting final parameters and provisioning) can be done automatically and on-demand in post-production instead of during production. This increases throughput, the predictability of throughput, and therefore reduces costs for the production line.
NFC can be used to:
- Geolocate parts that are stored in smart inventory systems.
- Configure many products simultaneously.
- Support the improved security of manufacturer provisioning (AKA Just In Time provisioning), but with the flexibility of doing this in post-production.
- Personalize the customer experience by market or any other parameter, for example, by specifying a language.
- Change parameters dynamically, for example, reconfigure a set of products for a different market if there is greater urgency.
- Allow trusted users to provision during the commissioning process.
- Simplify quality control — in some cases there is no need to open packages to complete checks.
Creating Value-Adds for End Users
Creating value for users is at the heart of Lean; the system is geared to eliminate anything that doesn’t achieve this goal.
Manufacturers can use NFC for all kinds of value-add features for end users, including authentication and tamper detection. NFC dynamic tags (also known as dual interface tags) can allow information about a product via a mobile app or ongoing condition monitoring and fault diagnostics to be rea.
Find out How NFC Can Give Your Organization an Edge
NFC tags are available in a wide variety of form factors. The NFC Forum has defined five different tag types to allow the usage of many different implementations of sizes, capacities, costs, and functionality. We can help you understand the opportunities that NFC can provide.
To interact with NFC tags there is a growing range of equipment supporting all types uses from configuration on a production line, to tracking during storage. For manufacturing personnel, NFC reader capability is present on the majority of smartphones on the market today – and there are over three billion smartphones in use today. NFC-equipped phones are available in almost every price category and even in hardened models that can be used as tools in harsh environments. For production environments, NFC reader/antenna combinations can be integrated into production lines to support mass writing of multiple tags. We are even seeing the arrival on the market of shelves and structures that integrate NFC reader capability for tracking products during storage via their NFC tag.
Learn more about NFC technology >

