What NFC does
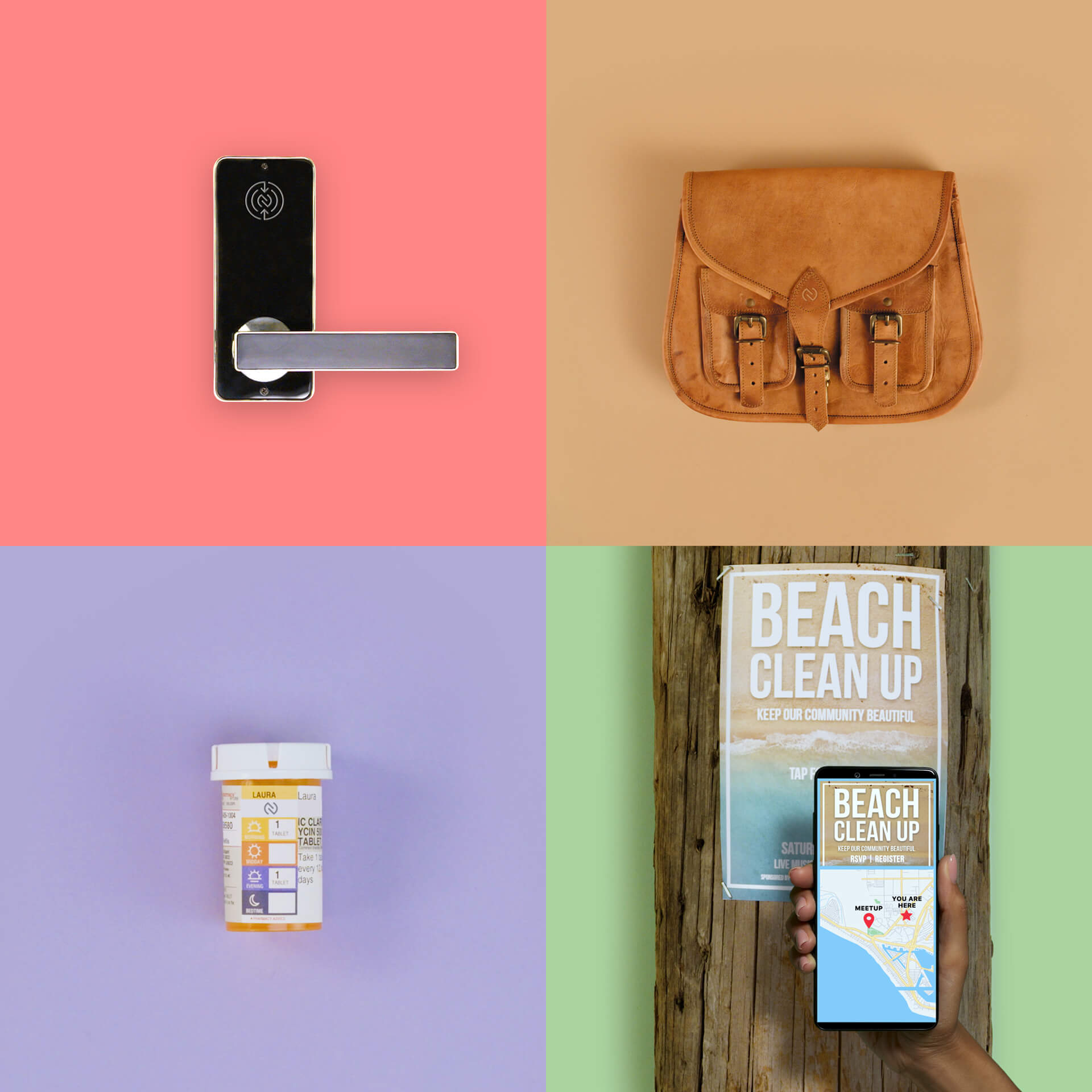
Where you'll find NFC
While you most often use NFC with your mobile phone, more and more form factors include NFC technology like:
Smart Watches
Tablets and their accessories
Affixed to syringes and prescription bottles
Jewelry, such as rings
Wireless Earbuds
Affordable “tags” made into apparel
NFC is also compatible with hundreds of millions of contactless cards and readers already deployed worldwide which means all you have to do is tap.

NFC & Other Wireless Technologies
Today there are many different wireless technologies that have replaced cable-based connections. Each are primarily differentiated by range, speed, power requirements, and security attributes. Using these factors, industries determine the applicability of each technology for hundreds of different use cases.
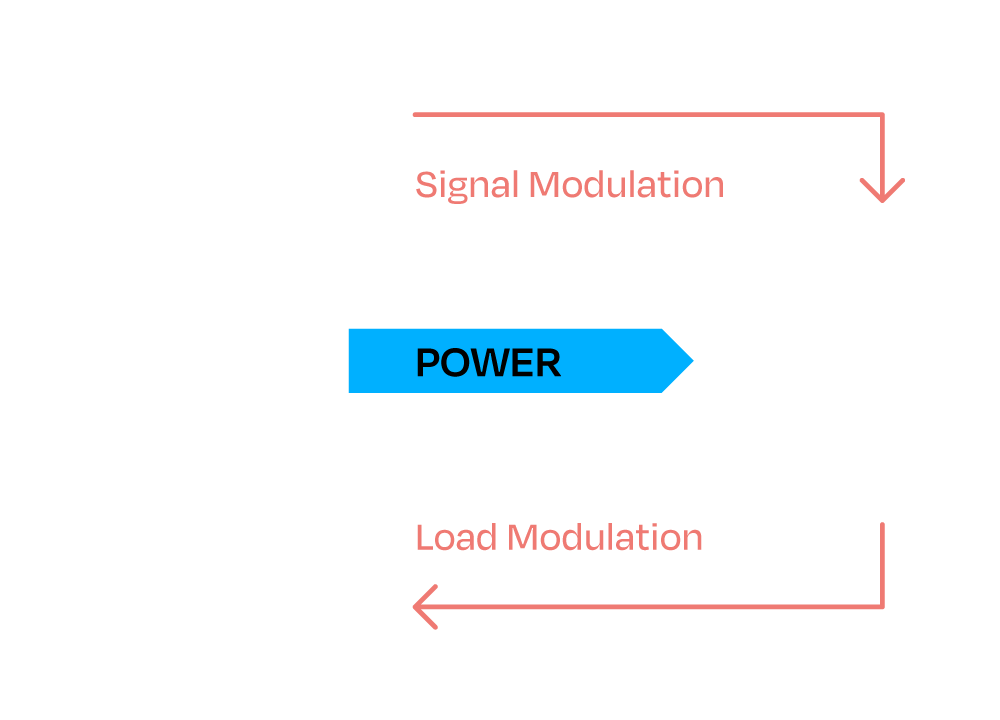
NFC is most suitable for ultra-short range (<2cm or one inch), low-latency startup, connect and transfer where only one side of the connection needs power. And unique to NFC, connections can exchange data or power. For the technically savvy, NFC Forum specifications operate in the 13.56 MHz band of unlicensed spectrum. Power harvesting has a maximum of 1w.

Digital keys provide the convenience and confidence we want when accessing our automobiles. The Car Connectivity Consortium, a global group of vehicle and consumer electronics companies developing an interoperable CCC Digital Key® technology, requires NFC Forum and other wireless technologies to provide a digital key solution that is secure and easy to use with all automobiles and smart devices.
As a complementary wireless technology it can be implemented to work with Bluetooth and Wi-Fi devices. Read more about Wi-Fi Easy Connect. It is often found along side Ultrawideband (UWB) and provides easy connectivity by other initiatives like Matter for the internet of things.



 Organizations may use NFC Forum marks to indicate the presence and location of NFC technologies in products and in conjunction with other related services. The NFC Forum N-Mark (Wayfinding) is the suggested option for this purpose. Full licensing details can be found
Organizations may use NFC Forum marks to indicate the presence and location of NFC technologies in products and in conjunction with other related services. The NFC Forum N-Mark (Wayfinding) is the suggested option for this purpose. Full licensing details can be found 